The key thing to remember when selecting the type of circuit for an electrical installation is the requirements stated in the IET Wiring Regulations. These are that:
- The number and type of circuits required for lighting, heating, power, control, signalling, communication and information technology, etc, shall be determined from knowledge of:
- Location of points of power demand.
- Loads to be expected on the various circuits.
- Daily and yearly variations in demand.
- Any special conditions, such as Harmonics.
- Requirements for control, signalling, communications and Information Technology etc.
- Anticipated future demand, if specified.
The best way to tackle this is breaking down an electrical installation to look at the different parts of it, and identifying the circuit types needed for each individual element. This can help with system reliability and cabling, as well as acknowledging that not all circuits in an installation will be working all of the time, and therefore current demand in some areas of the installation will be variable.
What are the characteristics of a lighting circuit?
A lighting circuit is a feature of most installations. They are usually rated at 6A but sometimes might be 10A or 16A. Lighting circuits appear in all installations and have a steady load when lights are operating. Lighting circuits can be wired three-plate, for circuits wired in composite cables (eg in domestic settings) or conduit method, for circuits wired in single-core cables within a suitable containment system.
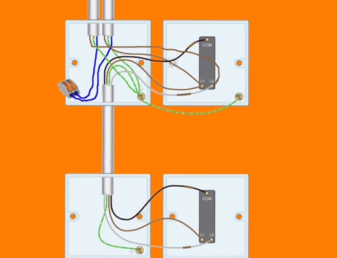
What is three plate wiring?
Lighting circuits wired in composite cables need more joints within the circuit, because composite cables limit the ability to take a single conductor from one point to another. These joints, or loop-ins, are usually a third live terminal within a light point, such as a ceiling rose. By incorporating loop-ins into the installation, individual cable cores can be extended elsewhere as necessary.
With a three-plate system, no junction box is used. The extra plate in the ceiling rose allows the circuit cable to be looped from ceiling rose to ceiling rose and the switch cable to be connected directly to the ceiling rose, effectively this makes the ceiling rose its own junction box.
What is two plate wiring?
With a two-plate wiring system, there is a junction box at each lighting position, into which is connected the circuit cable, the switch cable and the cable to the ceiling rose. The system gets its name because only two terminal blocks are needed.
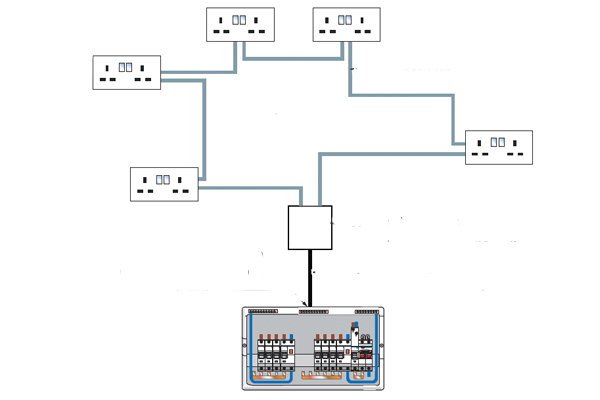
What are the characteristics of a power circuit?
Power circuits usually supply socket outlets but may also supply individual permanent appliances. They can be wired in two ways:
- Ring-final wiring – this has traditionally been the main method of wiring socket circuits in the UK, and allows a high number of outlets adjacent to their loads. In ring-final circuits, loads are shared by two parallel conductors which helps improve voltage drop because having the conductors run parallel reduces resistance. Ring-final wiring is not suitable for permanent loads, such as immersion heaters and care should be taken whilst using them when installing in kitchens – loads must be equally distributed around the circuit.
- Radial wiring – this is a mains power circuit of an appropriately rated cable which feeds into each power point and moves onto the next into one big line. The circuit ends with the last point on it. This form of wiring is becoming more popular with designers because it is much easier to determine faults than in a ring-final circuit – in a radial circuit if there is a break anywhere along the cable all the circuits after the break will stop working, while in a ring-final circuit even in case of fault all sockets will have power distributed to them – this makes for a risk of faults not being picked up, conductors being overloaded and then sparking an electrical fire.
What are the characteristics of alarm and emergency systems circuits?
Circuits for emergency systems need additional protection so they are not damaged in case of fault or fire. This kind of protection can include fireproof cabling and installing them totally separately from other circuits to ensure they are not affected by any faults.
What are the characteristics of data and control circuits?
Data cabling is often subject to interference between different wiring systems and need stronger earthing arrangements to overcome this. Therefore data and control circuits tend to be wired using different types of cable to the rest of a low voltage system.